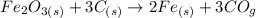
Firstly we have to convert the mass of the Fe2O3 to moles. We do this using the following equation:
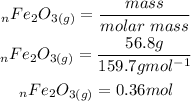
Based on the stichiometric ratio 1 mole of Fe2O3 reacts with 3 moles of carbon. Therefore 0.36 moles of Fe2O3 would react with x moles of carbon. We can determine x:
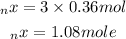
Now that we have found the moles of carbon reacted, we will now convert this moles to mass:
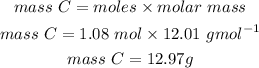
Mass of carbon required to react with 56.8g of Fe2O3 is 12.97g or 13.0g.