Answer:
a = 161.11 m/s²
Fnet = 2.74 N
Step-by-step explanation:
We know the distance traveled L = 1.16m and the time t = 0.12s, additionally, the initial velocity is vi = 0 m/s, so we can use the following equation to find the acceleration:
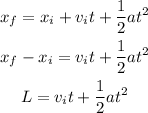
Replacing the values and solving for a, we get:
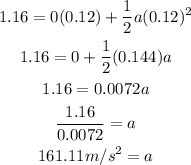
Then, the net force is equal to the mass times acceleration, so:
![\begin{gathered} F_{\text{net}}=ma \\ F_{\text{net}}=0.017\operatorname{kg}(161.11m/s^2) \\ F_{\text{net}}=2.74\text{ N} \end{gathered}]()
So, the answers are:
a = 161.11 m/s²
Fnet = 2.74 N