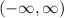The domain of a function is the set of all values that go into a function. Our function is
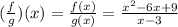
To find the domain, first let's rewrite the numerator as a product of binomials
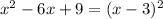
Then, our function is
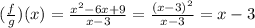
Our function is a line equation, and a line is defined everywhere, therefore, the domain of our function is