Linear Modeling
Any given situation is subject to be modeled as a linear function if the data follows the equation:
y = mx + b
Where m is the slope of the line represented by the dataset.
Suppose we know the line passes through points A(x1,y1) and B(x2,y2). The slope can be calculated with the equation:
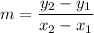
Let's pick two points from the table. For example, (5,2) and (7,4). The slope is:
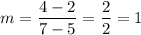
Now pick two other pair of points: (9,6) and (13,10):
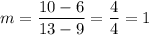
Regardless of the points we select, the slope is always 1, thus the table represents a linear model.
To find the model, we use the value of the slope:
y = x + b
Now we replace any of the given points, for example (11,8):
8 = 11 + b
Solving: b = -3
Thus the equation of the line is:
y = x - 3
The parent function of a line is y=x