The general form of an exponential function is expressed as
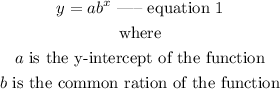
In the function
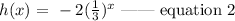
A) a-term:
In, the h(x) function, the a-term is -2.
B) the y-intercept:
The y-intercept of the function is obtained as the value of h(x), when x equals zero.
thus,
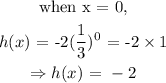
thus, the y-intercept is -2.
C) the common ratio
In equation 1, b is the common ratio of the exponential function. In comparison with equation 2, we have
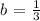
Thus, the common ratio of the function is
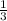
D) the x-intercept:
The x-intercept of the function is obtained as the value of x when h(x) equals zero.
thus,
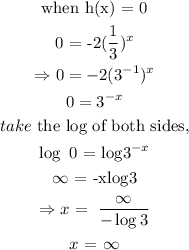
thus, the x-intercept is at ∞ (infinity).
E) the end behaviour:
The end behavoiur of the function is the behaviour of the h(x) function as x approaches plus infinity or negative infinity.
Thus,
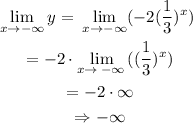

thus, as x tends to negative infinity, h(x) tends to negative infinity. when x tends to positive infinity, h(x) tends to zero.
Sketch of the h(x) graph on a coordinate plane:
The sketch of the h(x) function is as shown below: