So,
The reaction that we're performing is the next one:
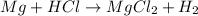
We need to balance it first:
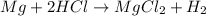
To balance, we verify that the number of atoms of each element in the reaction is the same before and after it occurs. As you can see, we have the same amount of atoms of each type before and after so the reaction is balanced now.
Now, we want to find the amount of Hydrogen gas (in liters) that we would obtain if we start with 0.11 grams of Mg. For this, we could follow the next steps:
Step 1. First, we should pass the 0.11 grams of Mg to moles of Mg. To do this, we divide by the molar mass of Mg:
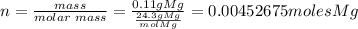
Step 2. Apply the stoichiometry of the given reaction and then use the fact that 1 mole of any gas is equal to 22.4L of the gas:

Therefore, we produce 0.1014 L of H2.
c. If the conditions are 23 Celsius and 105.2Kpa, we could use the ideal gas formula to find the theoretical volume of hydrogen gas.
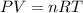
Remember that 23 Celcius = 296K and 105.2Kpa = 1,0382atm.
Now, if we replace:
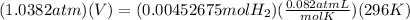
Solving for V, we obtain that the theoretical volume is:
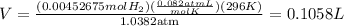
Which is approximately equal to the volume of the point b.