The trigonometric identity sin(x+y) is given by the following formula:
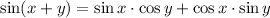
We need to find then cos(y), cos(x) and sin(y).
Other trigonometric identities we can use are:
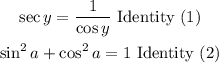
First, replace the sec(y) value and find cos(y):
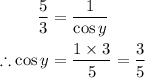
Now, apply the second identity to find cos(x) and sin(y):
![\begin{gathered} \sin ^2x+\cos ^2x=1 \\ \therefore\cos ^2x=1-\sin ^2x \\ \therefore\sqrt[]{\cos^2x}=\sqrt[]{1-\sin^2x} \\ \therefore\cos x=\sqrt[]{1-((1)/(4))^2} \\ \cos x=\sqrt[]{1-(1)/(16)^{}}=\sqrt[]{(1\cdot16-1\cdot1)/(16)} \\ \cos x=\sqrt[]{(15)/(16)}=\frac{\sqrt[]{15}}{\sqrt[]{16}}=\frac{\sqrt[]{15}}{4} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/db7gso16kxstp9q0m87crw9tujl5ypw63u.png)
And now sin y=
![\begin{gathered} \sin ^2y=1-\cos ^2y \\ \therefore\sin y=\sqrt[]{1-\cos ^2y} \\ \therefore\sin y=\sqrt[]{1-((3)/(5))^2} \\ \sin y=\sqrt[]{1-(9)/(25)}=\sqrt[]{(1\cdot25-1\cdot9)/(25)} \\ \sin y=\sqrt[]{(16)/(25)}=\frac{\sqrt[]{16}}{\sqrt[]{25}}=(4)/(5) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/zbrjlrfjx3m6g6wqddgc2fmaa8s426y95e.png)
Now, replace these values into the identity sin(x+y) and solve as follows:
![\begin{gathered} \sin (x+y)=\sin x\cdot\cos y+\cos x\cdot\sin y \\ \sin (x+y)=(1)/(4)\cdot(3)/(5)+\frac{\sqrt[]{15}}{4}\cdot(4)/(5) \\ \sin (x+y)=(1*3)/(4*5)+\frac{\sqrt[]{15}*4}{4*5} \\ \sin (x+y)=(3)/(20)+\frac{4\sqrt[]{15}}{20}=\frac{3+4\sqrt[]{15}}{20} \\ \sin (x+y)\approx0.925 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/z2u4msyyzfw09zj6zyvp8w7owqsqrae7ub.png)