2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(g) (1)
Don't forget to balance your reaction.
First, we need to determine which is the limiting reactant, H2 or O2.
Before we are doing this, we must assume STP conditions: temperature of 273 K (0° Celsius or 32° Fahrenheit) and the standard pressure of 1 atm.
Under these conditions, one mole of a gas occupies 22.4 L.
The Limiting Reactant:
Use stoichiometry and (1)
Remember: STP => 1 mol of gas = 22.4 L
2 x 22.4 L of H2 ----------- 22.4 L of O2
40 L of H2 ----------- x
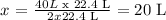
From this we say the limiting reactant is O2, we have exactly 20 L of this gas, and stoichiometry says that we need 20L.
The volume of water:
We use O2 to determine the volume of water,
22.4 L of O2 --------- 2 x 22.4 L of water
20 L of O2 --------- y
y = 40 L
Answer: 40L of water