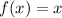
The y-intercept is the value of the function when it cross the y axis. When x is 0
In the parent function the y-intercept is 0
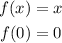
In g(x)
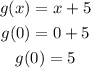
the y-intercept is 5. Respect to the parent function, y-intercept is 5 units up (in y-axis)
In h(x)
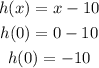
The y-intercept is -10. Respect to the parent function, y-intercpet is 10m units down (in y-axis)
In purple: parent function f(x)
In black: function g(x)
In red: function h(x)