Answer:
Left-hand derivative at x = -18 is -1
Right-hand derivative at x = -18 is 1
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the function;
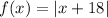
We'll use the below formula to find the left-hand derivative of the above function;
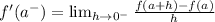
If we substitute and solve, we'll have;
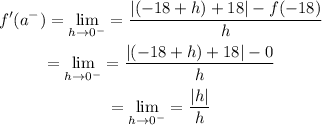
Since this is a left-hand derivative, therefore h < 0;
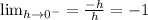
Let's go ahead and determine the right-hand derivative using the below formula;
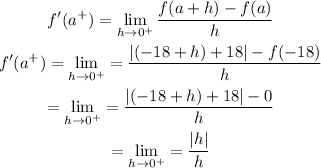
Since this is a right-hand derivative, so h > 0;
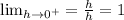
For a function to be differentiable at any point, its left-hand and right-hand derivative must exist and they must coincide.
From the above, we have that the left-hand derivative = -1 and the right-hand derivative = 1.