We need to find the expected number of callers whose calls last more than 20 minutes.
First, we need to find the percentage of expected calls that last more than 20 minutes and then multiply the result by the total of 10500.
We know that those calls are normally distributed with a mean of 16.3 minutes and a standard deviation of 4.2 minutes.
Thus, the percentage of those calls lasting more than 20 minutes is given by:
![\begin{gathered} P(x>20)=1-P(x\leqslant20) \\ \\ P(x>20)=1-P\left(z\operatorname{\leqslant}(20-16.3)/(4.2)\right) \\ \\ P(x>20)\cong1-P(z\operatorname{\leqslant}0.88095) \\ \\ P(x>20)\cong1-0.81083 \\ \\ P(x>20)\cong0.18917 \end{gathered}]()
Now, we need to multiply the above result by 10500. We obtain:
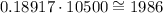
Therefore, approximating the result to the nearest unit, the expected number of callers whose calls last more than 20 minutes is:
Answer: 1986