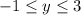Given:
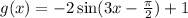
Find-: Domain and range.
Sol:
Domain-: The domain of a function is the set of its possible inputs, i.e., the set of input values where for which the function is defined. In the function machine metaphor, the domain is the set of objects that the machine will accept as inputs.
For the sin function, it accepts all real values of "x" then the domain is:
Range-: The range of a function is the set of outputs the function achieves when it is applied to its whole set of outputs. In the function machine metaphor, the range is the set of objects that actually come out of the machine when you feed it all the inputs.
Range of sin is -1 to +1
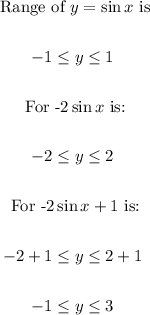
So, range is: