Answer:
The volume that the sample of oxygen would occupy at 25 ° C if the pressure were reduced to 760.0 torr is 40.2 L
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's law establishes the relationship between the pressure and the volume of a gas when the temperature is constant, so that the pressure of a gas in a closed container is inversely proportional to the volume of the container. That is, if the pressure increases, the volume decreases, while if the pressure decreases, the volume increases.
Boyle's law is expressed mathematically as:
Pressure * Volume = constant
or P * V = k
Considering an initial state 1 and a final state 2, it is true:
P1* V1= P2*V2
In this case:
- P1= 20.1 L
- V1= 1520 torr
- P2= 760 torr
- V2= ?
Replacing:
20.1 L* 1520 torr= 760 torr* V2
Solving:
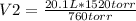
V2= 40.2 L
The volume that the sample of oxygen would occupy at 25 ° C if the pressure were reduced to 760.0 torr is 40.2 L