To answer the question we need the equation to calculate Ka (the acid dissociation constant).
For any acid we have the following dissociation equilibrium:
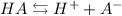
The Ka equation is the following:
![Ka=\frac{[H^+][{A^-}{]}^{{}{}{}}}{[HA]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/wkd5k1afgw6lh5l5xsi0s6lz0uunc2y3gg.png)
So to answer the question we need the concentration of the acid, which is 0.2M, of the protones, which is 9.86x10-4M, and the cation [A+].
As this is s monoprotic acid, [H+] is the same as [A+], which is 9.86x10-4M.
Now we calculate:
![Ka=\frac{[9.86x10^(-4)M][{9.86x10^(-4)M]}^{{}{}{}}}{[0.2M]}=4.86x10^(-6)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/xqodi3ayy9fgt9b8dgwkgl02qq0084qs0j.png)
So the Ka for this acid is 4.86x10-6 M.