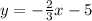The general form of a linear equation in the slope-intercept form is:
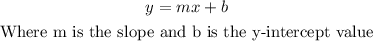
If the line we are looking for is parallel to y = -2/3 x + 1, so their slopes are the same, so m=-2/3 in the above equation.
And also we know that the line passing through the point (-6, -1), so:
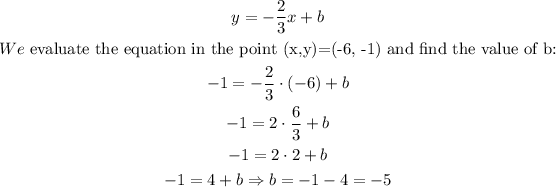
The equation of the line is: