7.41 m/s^2
Step-by-step explanationWhen an object is traveling in a straight line with an increase or decrease in velocity at equal intervals of time, then the object is said to be in uniform acceleration
to find the acceleration we can use the formulas
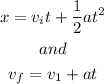
so
Step 1
a)
let
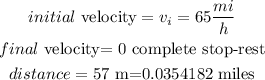
b) replace in equation (2)
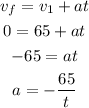
replace in equation (1)
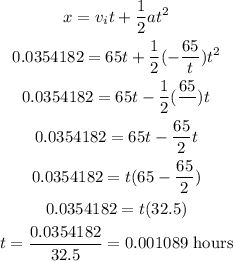
now, replace in the previous equation to find a
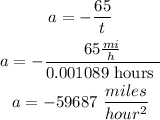
so, the answer is
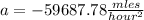
finally, let's convert the acceleration from miles per squared hour into meters per square second
remember that:
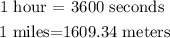
so
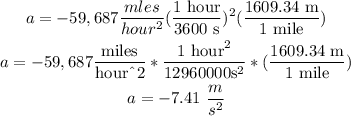
hence
the acceleration is -7.41 m/s^2
I hope this helps you