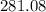For this exercise you can use the following formula:
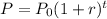
Where "P" is the final population, "r" is the rate of growth (in decimal form), "t" is time, and this is the initial population:
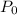
According to the information given in the exercise, the country's population in 2015 is 243 million. Then:
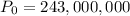
The rate of growth is 0.86%, so you need to divide it by 100 in order to express it in decimal form:
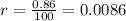
Since the must find the population in 2032, you can identify that:
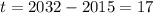
Then, substituting values into the formula and evaluating, you get:
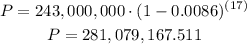
Therefore, the answer is, rounded to the nearest hundredth: