Answer:
C. The sum of square A and square B is equal to square C
Explanations:
From the diagram shown:
Thre squares, A, B, and C are joined at their vertices
The shape formed in between the vertices is a right-angled triangle
Using the Pythagora's theorem for the right-angled triangle:
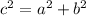
Since we are dealing with squares, and squares have all their sides equal.
This means that the rule will also apply to the areas identified with each of those squares
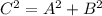
This can be interpreted as the sum of square A and square B is equal to square C