Answer:
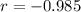
Explanation:
The Pearson correlation coefficient measures the strength of a linear association between two variables, where the value r=1 means a positive correlation and -1 a negative correlation.
It is represented by the equation:
![\begin{gathered} r=\frac{\Sigma(x_i-\bar{x})(y_i-\bar{y})}{\sqrt[]{\Sigma(x_i-\bar{x})^2}\sqrt[]{\Sigma(y_i-\bar{y)^2}}^{}} \\ \text{where,} \\ x_i=x\text{ values} \\ y_i=y\text{ values} \\ \bar{x}=\operatorname{mean}\text{ of x values} \\ \bar{y}=\operatorname{mean}\text{ of y values} \\ (x_i-\bar{x})(y_i-\bar{y})=\text{ deviation scores} \\ (x_i-\bar{x})^2\text{ and }(y_i-\bar{y)^2}=\text{ deviation squared} \end{gathered}]()
Then, find all the corresponding values and operate to find the correlation coefficient:
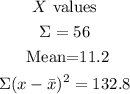
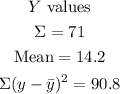
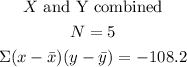
Now, using the formula for the coefficient:
![\begin{gathered} r=\frac{-108.2}{\sqrt[]{(132.8)(90.8)}} \\ r=-0.985 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/jx6vxj4iqefvt0fffqmh67yqx15w0sekj0.png)