The quadratic we are working with is;
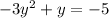
We can rewrite the equation in standard form as;
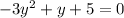
Comparing this with the standard form of a quadratic equation, we see that ;
a = -3 , b = 1 and c =5.
The discriminant from the solution formula is;
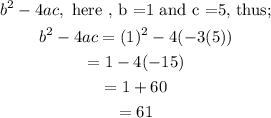
The discriminant is positive, therefore, there are 2 different real solutions to this quadratic equation.
Let us obtain these solutions, using the full quadratic formula;
![y=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/gfo69urp8rw17yg122uzk6md9epfe1uf75.png)
Let's insert the values of a, b and c to obtain;
![\begin{gathered} y=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt[]{61}}{-6} \\ y=\frac{-1+\sqrt[]{61}}{-6}\text{ and }\frac{-1-\sqrt[]{61}}{-6} \\ \text{simplified as} \\ y=\frac{1-\sqrt[]{61}}{6}\text{ and }\frac{1+\sqrt[]{61}}{6} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/mgtxvyvvr3kof2j1lxxbni1413jv9fo7oj.png)
Therefore, these are the solutions for y.