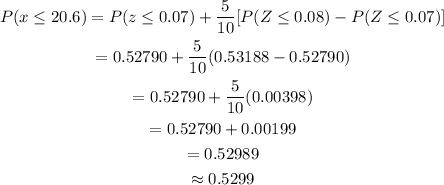For part (a), the mean of the sampling distribution is the same as the population mean. On the other hand, the standard deviation of the distribution is also given.
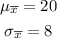
For part (b), notice that the sample size, n=64, is greater than 30. Thus, the shape must be a normal distribution. This means that the shape depends on the sample size.
Thus, the answer is option B.
For part (c), substitute the given values into the formula for z.
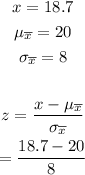
Simplify the expression.
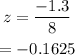
For part (d), we use the same procedure as part (c).
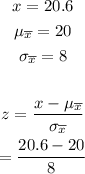
Simplify the expression.
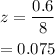
For part (e), to obtain the given probability, we must first find the z-score and then check the z-score table for the probability. Since we obtain the value earlier which is -0.1625, look for the value in the z-score table.
Notice that we don't have the exact value for -0.1625. We only have values for -0.16 and -0.17. Thus, we use the interpolation.

For part (f), since we already have the value for the z-score, look at the z-score table for the probability for the z-score which is less than or equal to 0.075.
Notice that we also do not have the exact value for 0.075. Thus, use the same procedure as part (e).