The first step is to determine the unit rate represented on the table.
If x and y have a direct relationship then
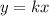
k represents the coefficient of variation (or unit rate)
k can be calculated as
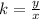
To determine the unit rate represented on the table use a set of values, for example (13, 21)
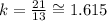
Now you have to determine the unit rate for each point on the graph and compare to the unit rate represented on the table.
Purple point
Coordinates (2,8)
Unit rate
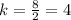
The unit rate is greater than the one expressed on the table.
Red point
Coordinates (3,9)
Unit rate
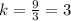
The unit rate is greater than the one expressed on the table.
Blue point
Coordinates (4, 10)
Unit rate
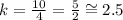
The unit rate is greater than the one expressed on the table.
Green point
Coordinates (5, 8)
Unit rate
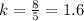
The unit rate is less than the one represented in the table by 0.005
Brown point
Coordinates (6, 7)
Unit rate
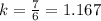
The unit rate is less than the one represented in the table.
Dark blue point
Coordinates (7, 6)
Unit rate
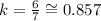
The unit rate is less than the one represented in the table.
The green (5,8), brown (6,7) and dark blue (7,6) points have a unit rate less than the one represented on the table.