First, we need to find the equivalent resistance. We can find it as follows:
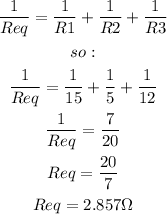
Now, we can find the voltage using Ohm's law:
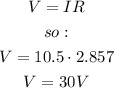
Now, since the circuit is in parallel, the voltage is the same for every resistance. So, let's find the current for each resistance using Ohm's law:
For the resistance of 15:
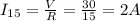
For the resistance of 5:
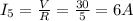
For the resistance of 12:
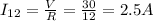
Completing the table using the previous data: