Answer:
![\tan X=\frac{3\sqrt[]{65}}{13}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/o7djim5pp4544rue1y5g5rnznynopc37l3.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
From the diagram:
• The side ,opposite, angle X is ZY
,
• The side ,adjacent to, angle X is XY
From trigonometric ratios, we know that:
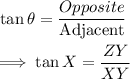
Since we require the value of ZY, we find it using Pythagoras Theorem.
![\begin{gathered} XZ^2=XY^2+ZY^2 \\ \sqrt[]{58}^2=\sqrt[]{13}^2+ZY^2 \\ ZY^2=58-13 \\ ZY^2=45 \\ ZY=\sqrt[]{45} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/3oawxbqoymxlym86pxmsyu3p722b59vgf2.png)
Therefore:
![\begin{gathered} \tan X=(ZY)/(XY) \\ =\frac{\sqrt[]{45}}{\sqrt[]{13}} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/1sj4ww9f6mtvi4angh6qlzue74547xxsh7.png)
We rationalize our result.
![\begin{gathered} =\frac{\sqrt[]{45}}{\sqrt[]{13}}*\frac{\sqrt[]{13}}{\sqrt[]{13}} \\ \tan X=\frac{3\sqrt[]{65}}{13} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/wzxs3egw62v6sx1j7o1ufyvh0la1o9jgtj.png)
•