Given:
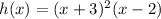
You can rewrite it as follows:
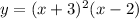
You can graph it by following these steps:
1. Find the x-intercepts. By definition, the value of "y" is zero when the function intersects the x-axis. Then, you need to make:
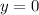
Substitute this value into the equation:
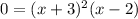
Solving for "x", you get:
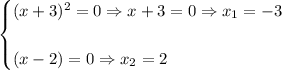
2. Identify the multiplicities:
- Notice that the first factor of the function is:
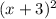
And has an exponent 2.
This means that:
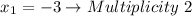
Since it has an even Multiplicity, the graph touches the x-axis, at that point, but it does not intersect it.
- Having the other factor:

Its exponent is 1. Then:
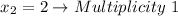
That even Multiplicity indicates that the graph intersects the x-axis at that point.
3. Find the y-intercept. By definition, the value of "x" is zero when the function intersects the y-axis. Then, you need to make:
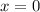
Substitute this value into the function and solve for "y":
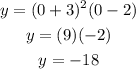
4. By definition, the end behavior of a function can be determined knowing its Leading Coefficient and its degree. Then, you need to follow these steps to find the end behaviors of the function:
- Expand the right side of the equation. Remember this formula:
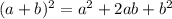
Then, you get:
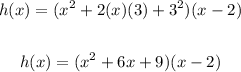
Multiply the polynomials by applying the Distributive Property:
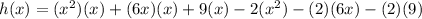
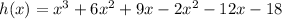
Add the like terms:
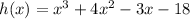
Knowing that the degree is the highest exponent and that the Leading Coefficient "a" is the number that multiplies the term with the highest exponent, you can identify that:
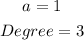
By definition, if:
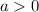
The end behaviors of a function are:
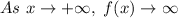
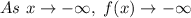
Therefore, in this case, since the Leading Coefficient is positive, you can determine that as "x" approaches positive infinity, h(x) approaches positive infinity:
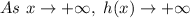
And as "x" approaches negative infinity, h(x) approaches negative infinity:
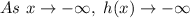
Knowing all the data found, you can graph the Cubic Function.
Hence, the answers are:
• x-intercepts:
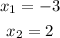
• y-intercept:
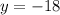
• Multiplicity:
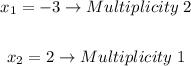
• End behaviors:
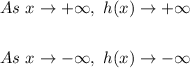
• Graph: