Let us first define what the molarity is, the molarity corresponds to the moles of solute over the liters of the solution, the respective equation will be:
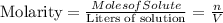
In this case, the molarity is equal to 0.5M.
We see that we have two unknowns, the volume and the number of moles. Moles can be found using the given grams and the molar mass of glucose as follows:
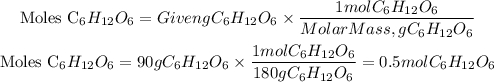
Now, since we have the moles of solute and the molarity of the solution, we can find the volume by clearing it from the first equation:
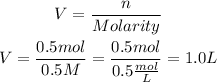
So, the volume of the solution will be 1.0 liter.
The answer will be the first option 1.0L