The question requires us to calculate the molar concentration of an acetic acid solution, given that it was necessary 36.4 mL of a 0.100 M NaOH solution to neutralize 50.0 mL of the acid.
The following information was provided by the question:
concentration of NaOH solution = C(OH-) = 0.100 M
volume of NaOH solution = V(OH-) = 36.4 mL
volume of CH3COOH solution = V(H+) = 50.0 mL
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) react according to the following reaction:
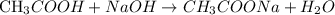
Considering that at the equivalent point the number of moles of acid (H+) is the same as the number of moles of base (OH-) and taking the stoichiometry of the reaction into consideratio (1 : 1), we can write:
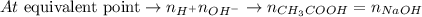
We can also write the number of moles of a compound (n) in terms of its molar concentration and volume:
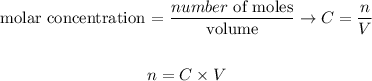
Thus, considering the equivalent point, we can say:
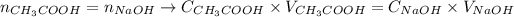
Now, we can apply the values of volume and concentration provided by the question to the equation above and obtain the concentration of the acid:
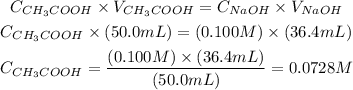
Therefore, the molar concentration of the acetic acid solution is 0.0728 M and the best option to answer this question is the third one.