We will investigate how to use the difference of two squares theorem to determine a solution to the equation.
The equation at hand is as follows:
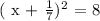
We will move all the terms on the left hand side of the " = " sign as follows:
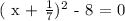
The difference of two squares theorem states that:
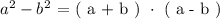
We see from the above form that we have the following:
![\begin{gathered} a\text{ = x + }(1)/(7) \\ \\ b\text{ = }\sqrt[]{8} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/rg8q0diii9y4v59ucjwb6el47vr31j1897.png)
Using the difference of two squares formulation we can re-write as a multiple of two factors:
![(\text{ x + }(1)/(7))^2\text{ - 8 }\equiv\text{ ( x + }(1)/(7)\text{ + }\sqrt[]{8}\text{ ) }\cdot\text{ ( x + }(1)/(7)\text{ -}\sqrt[]{8}\text{ )}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/l8hlzp744xths0kf4hfhl93z8t72k13xh4.png)
Then the factorized equation becomes:
![\text{ ( x + }(1)/(7)\text{ + }\sqrt[]{8}\text{ ) }\cdot\text{ ( x + }(1)/(7)\text{ -}\sqrt[]{8}\text{ ) = 0}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/mo5y43zv6nxh0rp7delm63aenqiq8313d7.png)
The solution of the equation becomes:
![\begin{gathered} x\text{ = - }(1)/(7)\text{ - }\sqrt[]{8} \\ \\ x\text{ = }\sqrt[]{8}-(1)/(7) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/rqpnj6nga9im9nrnnnt1zfxbbv0qggz6rw.png)
We can condense our solution in the form:
![x\text{ = - }(1)/(7)\pm2\sqrt[]{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/vn0b5ut92sawter8r2urmfwtpzbd80ssm0.png)