Solution
Given
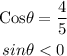
Required
To find the quadrant of terminal side of θ and sinθ
Step 1
Find the opposite
Using the trig ratio CAH(cosine, adjacent, hypothenuse)

We can find the opposite using pythagoras theorem, which is expressed as
![\begin{gathered} \text{hypothenuse}^2=opposite^2+adjacent^2 \\ 5^2=opposite^2+4^2 \\ \text{opposite}=\sqrt[]{25-16} \\ \text{opposite = }\sqrt[]{9} \\ \text{opposite = 3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/qcgbjsh5vng84zgxx2bmtv16yktnujjdbf.png)
Step 2
Find sinθ
Using the trig ratio SOH (sine, opposite ,hypothenuse), we can find sinθ as follows
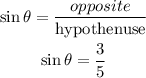
Final Step
Find the quadrant of the terminal side of θ and sinθ
Since sinθ <0, this means that sinθ is negative
Therefore the right answer is
sinθ = 3/5 and it is in quadrant IV because that is where cosine is positive..
Final answer: option A