We have to calculate the cosine of an angle using the value of its sine. For this purpose we can use the following relation that is met for any angle:
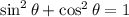
Then, the cosine is given by:
![\begin{gathered} \sin ^2\theta+\cos ^2\theta=1 \\ \cos ^2\theta=1-\sin ^2\theta \\ \cos \theta=\sqrt[]{1-\sin^2\theta} \\ \lvert\cos \theta\rvert=\sqrt[]{1-((1)/(4))^2}=\sqrt[]{1-(1)/(16)}=\sqrt[]{(15)/(16)} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/a07ypyztb26bp28o6elsbo18veybt6c8z4.png)
This means that the cosine is either:
![\sqrt[]{(15)/(16)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8xf4nz56r06lnysrswxgwf9vjsuqxsbmq2.png)
or:
![-\sqrt[]{(15)/(16)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/4tqui0tzii8qyboqjqmsivznx086tmzmzy.png)
Since the angle theta is between 90° and 180° then its cosine must be a negative number then:
![\cos \theta=-\sqrt[]{(15)/(16)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/u8rovb50pvi6zug23oyr4nal2i6yn2z7oj.png)