Answer:
V1/T1 = V2/T2.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's remember Charles's Law: Charles's Law states that the volume of a given mass of gas varies directly with the absolute temperature of the gas when pressure is kept constant.
Wher
Mathematically, this can be described like this:
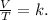
We can use Charles's Law to compare changing conditions of gases, like this:
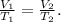
Where V is volume, T is the temperature, subindex 1 indicates the initial conditions, and subindex 2 indicates the final conditions.
The answer would be V1/T1 = V2/T2.