Answers:
![\begin{gathered} y=\frac{7-\sqrt[]{21}}{14} \\ or \\ y=\frac{7+\sqrt[]{21}}{14} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/a5qkbmvsufrb7iii71y0xepet2itvxnbft.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
To use the quadratic formula, the equation should have the following form:
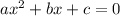
So, a is the number beside the y^2, b is the number beside y and c is the constant value.
Then, subtracting 1 from both sides of the equation, we get:
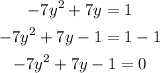
Therefore, the value of a is -7, the value of b is 7 and the value of c is -1. So, the discriminant is equal to:
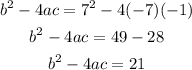
Since the value of the discriminant is positive, we have two different real solutions. So, we can solve the quadratic equation as follows:
![\begin{gathered} y=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a} \\ y=\frac{-7_{}\pm\sqrt[]{21}}{2(-7)}=\frac{-7\pm\sqrt[]{21}}{-14} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/y6fda2lhuf0id6ubw4y6a1h8t1wgy3i9eo.png)
Therefore, the solutions of the equation are:
![\begin{gathered} y=\frac{-7+\sqrt[]{21}}{-14}=\frac{7-\sqrt[]{21}}{14} \\ or \\ y=\frac{-7-\sqrt[]{21}}{-14}=\frac{7+\sqrt[]{21}}{14} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/1w4wppve4u4th136r0cdqo81nfs7b7t3yn.png)