The change in kinetic energy of the car as it drives up the hill is 3.53 x
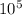 J.
J.
The work-energy principle states that the net work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
To find the change in the car's kinetic energy from the bottom of the hill to the top, we can apply the work-energy principle that states the change in kinetic energy (ΔKE) equals the net work done on the object:
ΔKE = Work by the engine + Work by friction
According to the problem, the work done by the engine is 6.64 x
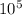 J and the work done by friction is -3.11 x
J and the work done by friction is -3.11 x
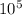 J. Putting these values into our equation gives us:
J. Putting these values into our equation gives us:
ΔKE = (6.64 x
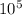 J) - (3.11 x
J) - (3.11 x
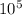 J) = 3.53 x
J) = 3.53 x
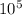 J
J
Therefore, the change in the car's kinetic energy as it drives up the hill is 3.53 x
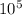 J.
J.