The slope of the given equation is
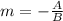
Where A = 2, and B = 1.
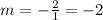
But, the slope is equal to the tangent function:
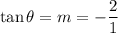
If we consider this tangent function about a right triangle, then the opposite leg is 2, and the adjacent leg is 1. Using Pythagorean's Theorem, we find the hypothenuse.
![\begin{gathered} h^2=2^2+1^2 \\ h=\sqrt[]{4+1} \\ h=\sqrt[]{5} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/r6v11v46tmsywfzxn8lv830ivqp138nrup.png)
So, the sine function is
![\sin \theta=\frac{2}{\sqrt[]{5}}\approx0.89](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/fvklrqlxm057suqau4lfmvgv65mvsqriab.png)
And, the cosine function is
![\cos \theta=\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{5}}\approx0.45](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/3xk0idn9f21flbk56cdsd1gpg04guu04ur.png)
The inverses are
![\begin{gathered} \cot =(1)/(2) \\ \sec =\frac{\sqrt[]{5}}{1}\approx2.23 \\ \csc =\frac{\sqrt[]{5}}{2}\approx1.12 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/e16vj9spf73486hlydf0ralpmytlygacre.png)