Given:
a.) Garden canes have lengths that are normally distributed with a mean of 208.5 cm.
b.) Standard deviation of 2.5 cm.
c.) Probability of the length of a randomly selected cane being between 205cm and 210cm.
Step 1: Determine the z-score of two measures (205 cm and 210 cm).
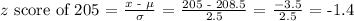
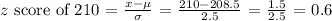
Step 2: Let's determine the equivalent probability of each computed z score.
For 205 cm:
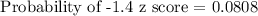
For 210 cm:
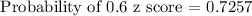
Step 3: Subtract the two probabilities.
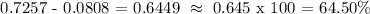
Therefore, the probability of the length of a randomly selected cane being between 205cm and 210cm is around 64.50% or 0.645
Below are the table applied to determine the respective probabilities on a given z score: