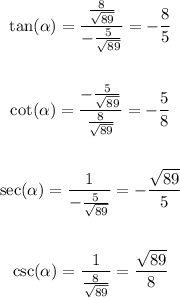The points on the terminal side of an angle α can be described as:
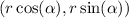
Where r is the distance from the origin to the point. Find r for the point (-5,8):
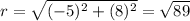
Then:
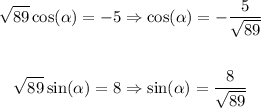
Recall the definitions of the tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant of an angle in terms of its sine and its cosine:
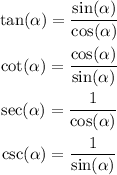
Replace the expressions for cos(α) and sin(α) to find the values of tan(α), cot(α), sec(α) and csc(α):