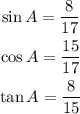A diagram of the right triangle ABC with right angle at C is shown in the following image:
We are going to assume that side a is opposite to angle A, side b is opposite to angle B, and that side c is opposite to angle C:
We are asked to find sinA, cosA, and tanA.
First, let's remember the definitions for sine, cosine, and tangent for any angle X:
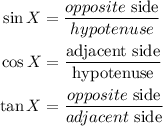
In this case, for angle A:
The opposite side to angle A is a=8
The adjacent side to angle A is b=15
The hypotenuse is c=17.
Substituting these values to find the sine of A:
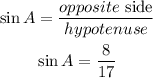
We do something similar to find the cosine of A:
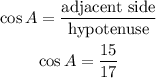
And finally, the tangent of A is:
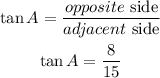
Answer: