Given:
The voltage applied,
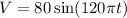
The resistance of the resistor, R=24.0 Ω
To find:
The reading in the ammeter.
Step-by-step explanation:
An ac ammeter connected in series with the resistor reads the root mean square value of the current, i.e., I_rms.
Comparing the given equation of the voltage to the standard equation,
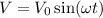
We get, V₀=80 V
The root mean square value of the voltage is given by the equation,
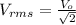
On substituting the known values,
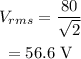
Thus the value of I_rms is calculated by the equation,
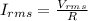
On substituting the known values,
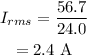
Final answer:
Thus the reading of the ac ammeter connected in series with the resistor is 2.4 A.