We have a table that relates GMAT with GPA.
We have to calculate the correlation coefficient (r).
The formular for r is:
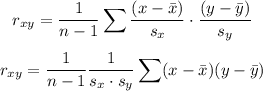
sx will be the standard deviation of the sample of GMAT, while sy will be the standard deviation of the sample of GPA.
Using software, we can calculate the mean and standard deviation of both variables:
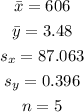
Then, we can calculate r as:
![\begin{gathered} r_(xy)=(1)/(n-1)(1)/(s_x\cdot s_y)\sum ^{}_{}(x-\bar{x})(y-\bar{y}) \\ r_(xy)=(1)/(5-1)\cdot(1)/(87.063\cdot0.396)\sum ^{}_{}(x-606)(y-3.48) \\ r_(xy)=(1)/(4)\cdot(1)/(34.497)\sum ^{}_{}(x-606)(y-3.48) \\ r_(xy)=(1)/(137.99)\lbrack(660-606)(3.7-3.48)+(580-606)(3-3.48)+(480-606)(3.2-3.48)+(710-606)(4-3.48)+(600-606)(3.5-3.48)\rbrack \\ r_(xy)=(1)/(137.99)\lbrack54\cdot0.22+(-26)\cdot(-0.48)+(-126)(-0.28)+(104)(0.52)+(-6)(0.02)\rbrack \\ r_(xy)=(1)/(137.99)\lbrack11.88+12.48+35.28+54.08-0.12\rbrack \\ r_(xy)=(113.6)/(137.99) \\ r_(xy)\approx0.823 \end{gathered}]()
The correlation coefficient is r = 0.823, which indicates a strong positive correlation, as the value of r is within the interval 0.7 and 0.9.
Now, we have to find the linear regression model to relate the two variables.
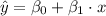
Then we can calculate the coefficients as:
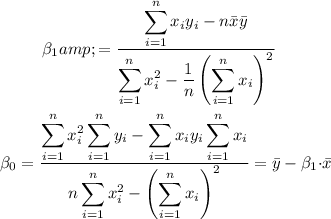
We can calculate the coefficients as:
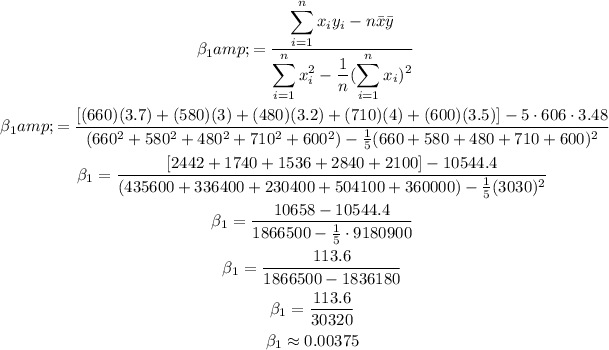
Now we can calculate the y-intercept of the regression model as:
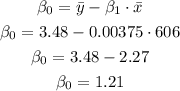
Then, we can write the regression model as:
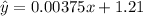
We can graph this with points as:
We can use the model to predict values of GPA for an specific value of GMAT.
If GMAT = 500, then we predict a value of GPA of:
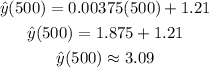
We can use this model to predict the GPA for a GMAT score of 580 as:
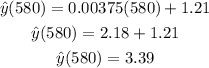
The data point for GMAT = 580 indicates a GPA of 3, so the regression model estimates a higher value of GPA in this case (the actual value is lower than the predicted value).
Answer:
a) r = 0.823
b) The correlation is strong and positive.
c) y = 0.00375x + 1.21
d) GPA = 3.09
e) Lower