Given:
D1 = 2 m
D2 = 4 m
Distance between object and lens = 1 m
Let's find where the image will appear relative to the second lens.
To find the distance, apply the formula:
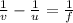
Thus, we have:
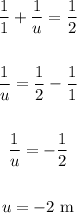
Now, we have the equation:
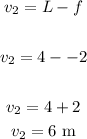
Now, let's use the Lens equation:
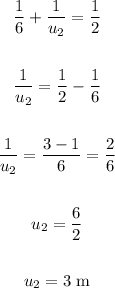
Now, to find the image distance relative to the second lens, we have:
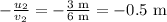
Therefore, the image will appear -0.5 m relative to the second lens.
ANSWER:
1.) -0.5 m