The given equation is
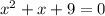
To complete the square, first, we have to move the independent term to the other side.
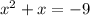
Then, we divide the linear coefficient by 2, then we apply a square power to it.
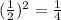
We add this fraction to each side.
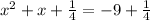
Then, we factor the trinomial and sum the numbers on the right side.
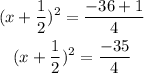
Then, to solve for x, we use a square root on both sides.
![\begin{gathered} \sqrt[]{(x+(1)/(2))^2}=\pm\sqrt[]{-(35)/(4)} \\ (x+(1)/(2))=\pm\sqrt[]{-(35)/(4)} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/9sab1a4st8tog0uglfo4zkrx5tpoobu3fm.png)
As you can observe, the equation has no real solutions because the square root of a negative number can be solved in the real numbers.
Hence, the equation has no real solutions, and the number added to complete the square is 1/4.