A series that has a finite sum is called convergent series. Otherwise, are divergent.
• Direct Comparison Test
Supposing that aₙ ≥ 0 and bₙ ≥ 0 for all values of n.
• Converges:, If aₙ ≤ bₙ for all values of n and
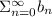
converges, then the series:
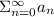
also converges.
• Diverges: ,If aₙ ≥ bₙ for all values of n and
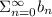
diverges, then the series:
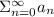
also diverges.
Our series:
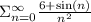
Applying the comparison we can see that the series converges.
Answer: converge.