Given:
The objective is to find the probability of getting a total of 2 in tossing a pair of dice.
Since each dice contain 6 sides. So the sample space in rolling two dices is,
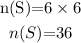
The sample space of getting sum of 2 is,
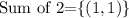
Thus, the number of sample space of getting a sum of 2 is one.
Then, the probability of getting a sum of 2 in rolling a pair of dice is,
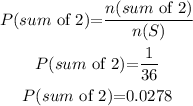
Hence, option (A) is the correct answer.