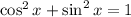Given the equation:
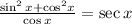
Let's determine the trigonometric identity that you could be used to verify the exquation.
Let's determine the identity:
Apply the trigonometric identity:
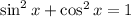
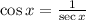
Replace cosx for 1/secx
Thus, we have:
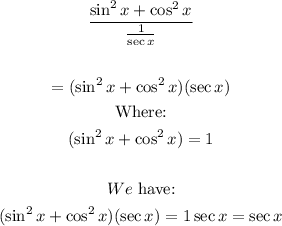
The equation is an identity.
Therefore, the trignonometric identity you would use to verify the equation is:
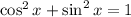
ANSWER: