ANSWER and EXPLANATION
1. We want to find the center of the given equation:
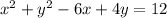
To do this, complete the square for the two variables in the equation, x and y:
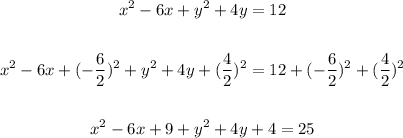
Now, factorize the x and y parts of the equation and write the equation of the circle in general form:
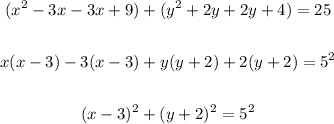
In the general form of the equation of a circle:
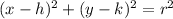
the center of the circle is (h, k).
Therefore, comparing the given equation to the general equation of a circle, the center of the circle is:
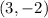
2. Now, we want to graph the circle. The graph of the circle is given below:
3. To find the x and y-intercepts of the circle, we have to find the points where the graph of the circle touches the x and y axes.
For the y-intercepts:
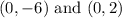
That is the answer.
Since we want to write the x-intercepts in radical form, we can solve for them from the given equation.
To find the x-intercepts, solve for x when y is equal to 0:
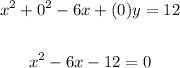
Solve using the quadratic formula:
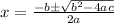
where a = 1, b = -6, c = -12
Therefore, the x-intercepts are:
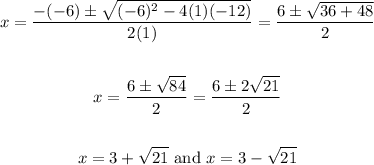
Those are the x-intercepts in radical form.