Part A.
If the significance level is 0.05, the conclusion depends on the P-value.
If the P-value is below 5%, the null hypothesis is rejected.
The P-value for this right-tailed test and z=2.52 given from z table is:
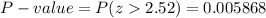
Decision:
You can reject H₀ at the significance level 0.05, because your p-value does not exceed 0.05.
Part B.
In this case, the significance level is 0.01 and, as the alternative hypothesis is defined with an unequal sign, the test is two-tailed.
This changes the way we calculate the P-value, as we need to compute the two tails.
The P-value is:
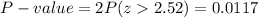
Decision:
The P-value is bigger than the significance level, so the effect is not significant and the null hypothesis is failed to be rejected.