Step 1
Given the triangle, ABC translated to A'B'C'
Required to find the algebraic description that maps triangle ABC and A'B'C'
Step 2
The coordinates of points A, B,C are in the form ( x,y)
Hence

Step 3
Find the algebraic description that maps triangle ABS TO A'B'C'

The algebraic description is found using the following;
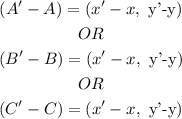
Hence,
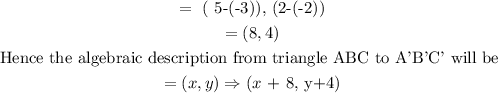
Hence the answer is option B