To determine the material requiring the smallest applied force for a 10-kilogram block sliding at constant velocity, we'll use the formula:
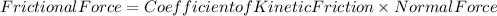
The normal force (N) is equal to the weight of the object
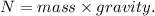
For a 10-kilogram block,
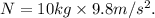
Let's assume Material A has the lowest coefficient of kinetic friction. The force required (F) is given by:
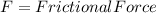
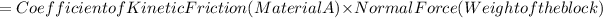
By plugging in the values, we can calculate the force for each material:
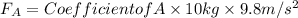
Repeat this process for Materials B, C, and D. The material with the smallest calculated force will require the least applied force to maintain constant velocity.