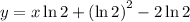Answer:
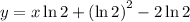
Explanation:
Differentiation is an algebraic process that finds the gradient of a curve.
At a point, the gradient of a curve is the same as the gradient of the tangent line to the curve at that point.

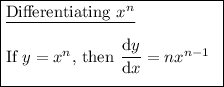
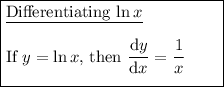
Differentiate the given function using the chain rule:
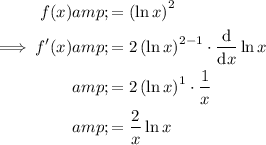
To find the gradient of the function at x = 2, substitute x = 2 into the differentiated function:
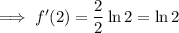
Therefore, the gradient of the function at x = 2 is ln(2).
Substitute x = 2 into the function to find the y-value of the point on the curve when x = 2:
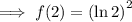
Slope-intercept form of a linear equation:
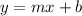
where:
- m is the slope.
- b is the y-intercept.
Substitute the point (2, (ln 2)²) and the found gradient into the slope-intercept formula and solve for b:
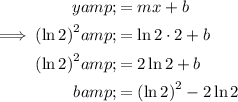
Therefore, the tangent has the equation: