Answer:
C
Explanation:
Since PT = QT , then Δ PQT is isosceles with the 2 base angles congruent.
∠ PQT =
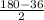 = 72°
= 72°
∠ TQR = 180° - 72° = 108° ( adjacent angles on a straight line )
Since QT = QR , then Δ QRT is isosceles with 2 base angles congruent
∠ QTR = ∠ QRT =
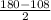 =
=
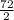 = 36°
= 36°
∠ TRS = 180° - 36° = 144° ( adjacent angles on a straight line )
Since RT = RS , then Δ TRS is isosceles with 3 bas angle congruent
∠ RTS = ∠ RST =
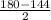 =
=
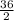 = 18°
= 18°
Then
∠ PTS = ∠ PTQ + ∠ QTR + ∠ RTS = 36° + 36° + 18° = 90°